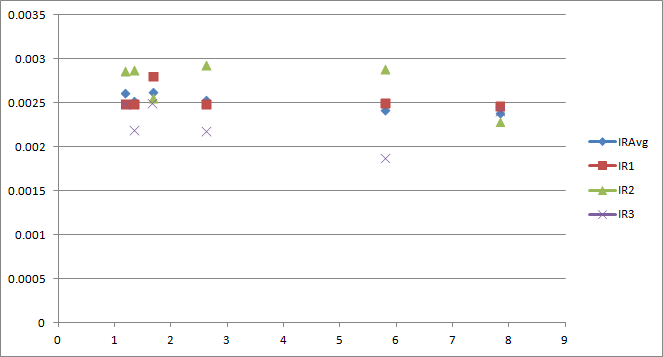
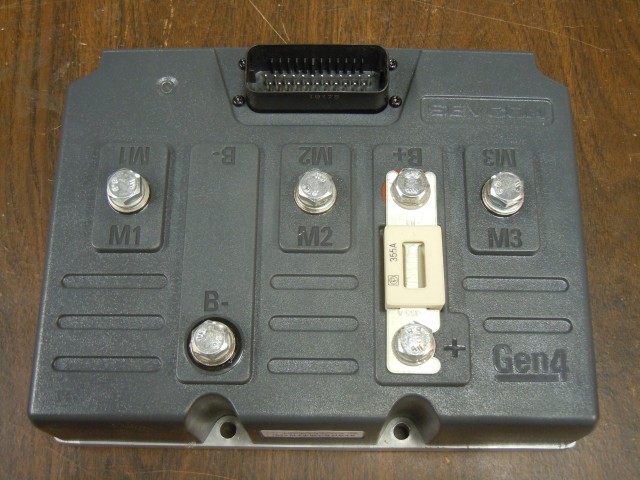
Here’s a look inside a Sevcon Generation 4 AC motor controller. This particular one is the 80V 350A model, sourced for the ArcWolf racing go-kart. Two were purchased from an eBay seller in located in Korea for US$720 total including shipping.
Imgur album of all teardown photos
The controller is waterproof with a plastic shell over an aluminum base plate. Terminals protrude through the top.

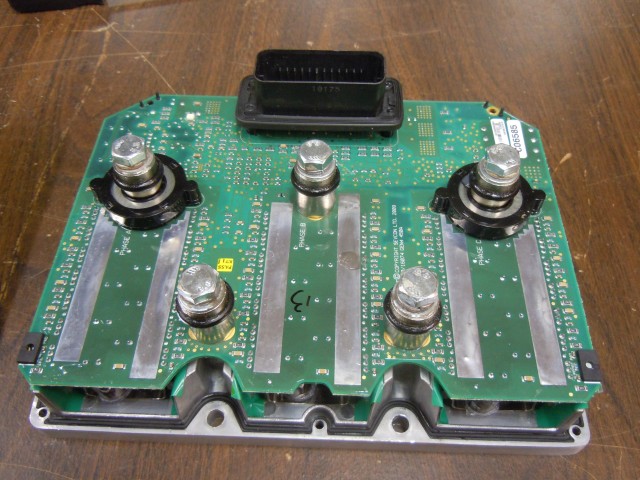
With the screws removed, the top comes off with prying.

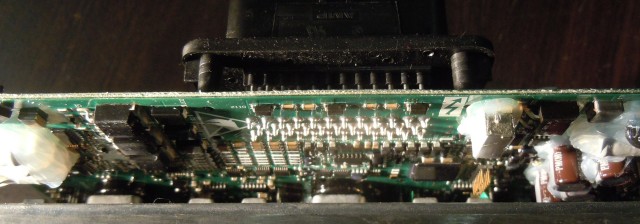
Just one big board. Surprisingly there are no bus bars, the 350A connections go directly to the PCB! The three half bridges are clearly visible. Each leg uses seven IPP075N15N3 G 150V 7.5mOhm FETs.
The PCB is at least four layer. The top and bottom layers both carry the current from the FETs to the 3 phase outputs, with the DC bus running on inner layers. The number of inner layers is not known.

The FETs are clamped to the heatsink by spring clamps. These must be held open with a special jig during assembly while the top board is inserted.
A green thermal interface material couples heat to the heatsink. The material is basically a think Kapton sheet with a phase change material that melts at high temperature. I recall using this material in an AC inverter I built years ago because it was the highest performance economical material available. It likely still is to this day.
The bus capacitors are Nichicon 160V 100uF with 8 per leg (2400uF total). The capacitors and other weak components are secured with silicone to stop them from breaking off due to vibration.
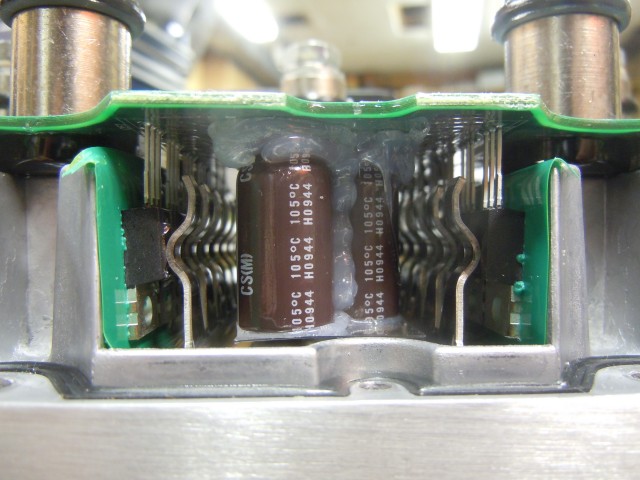
Current sensing is accomplished with hall effect current sensors. These are simply a slotted toroidal magnetic core around the power conductor. The slot concentrates the magnetic field, allowing a hall effect sensor in the slot to sense the magnetic flux which is proportional to the current. The gap / hall sensor is under the clear silicone.
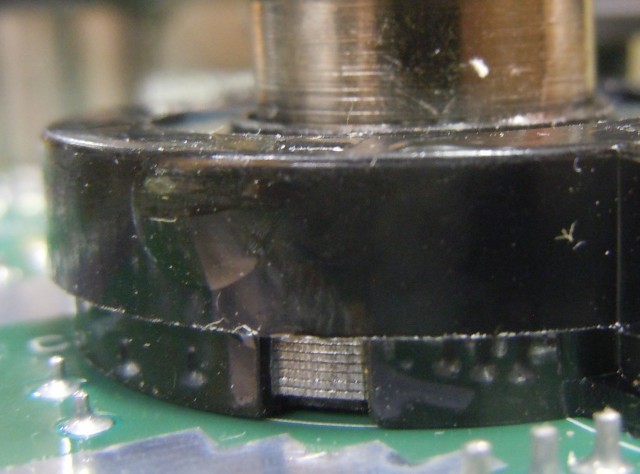
The magnetic laminations are visible. For high current applications ferrite may saturate, so iron laminations are used instead.
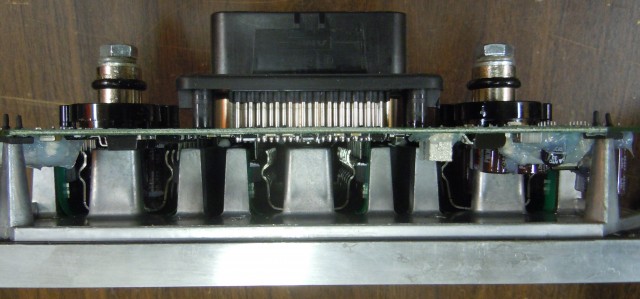
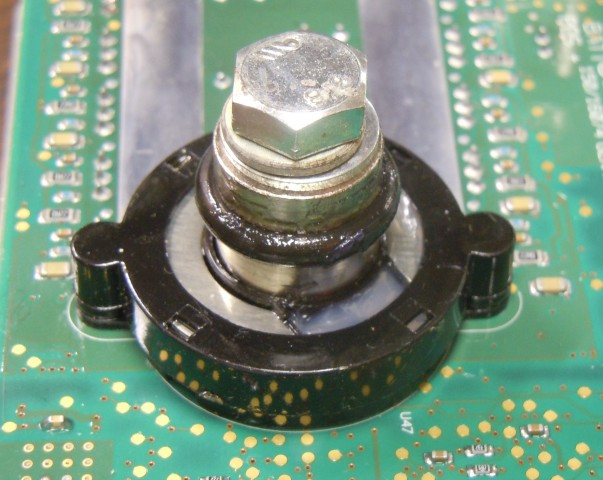
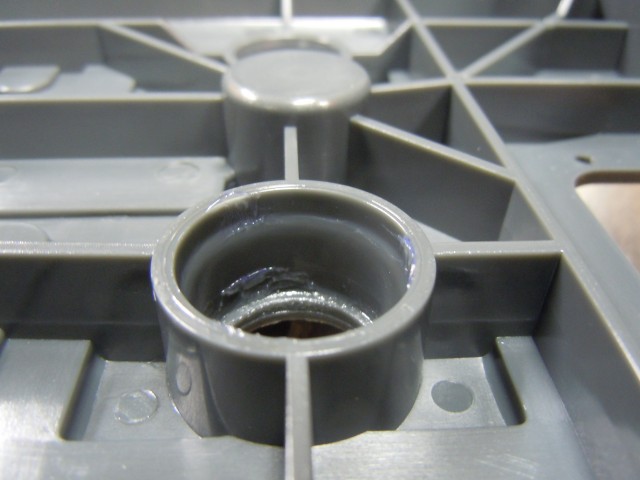
Terminals are sealed with o-rings. Grease is applied presumably to ease assembly and to improve sealing.

The logic section of the board is hard to see without removing the entire board. There’s not too much here, a large amount of IO protection near the connector, a switching power supply to the right, and what I believe are contactor drivers on the left.
The main micro is a TMS320F2811 32-bit 150MHz device, quite powerful!
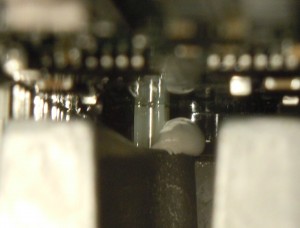
Heatsink temperature is sensed by two thermistors mounted to the main PCB and inserted into holes in the main heatsink. There are no wires in the entire design, leading to very easy and low cost assembly.
The case is sealed to the base by a o-ring-like moulded rubber seal


Overall a very elegant and easy to assemble design.